Factors in the selection of mining system are:
1. Room nature of ore deposits
a. Size (dimensions : height
or thickness in particular) b. Shape (tanular, pliable, massif, irregular)
c. Position (tilted, flat or
upright) d. Depth (average value, stripping ratio)
a. Size (dimensions : height
or thickness in particular) b. Shape (tanular, pliable, massif, irregular)
c. Position (tilted, flat or
upright) d. Depth (average value, stripping ratio)
2. Geological and Hydrological Conditions
a. Mineralogy and petrology (sulfide
or oxide) b. Chemical composition (main, by-product,
mineral by product)c. Sediment structure (creases, faults, intrusions, discounting)
d. Weak field (stocky, fracture, cleavage in minerals, cleats in Coal)
e. Uniformity, alteration,
erosion f. Groundwater and hydrology
a. Mineralogy and petrology (sulfide
or oxide) b. Chemical composition (main, by-product,
mineral by product)c. Sediment structure (creases, faults, intrusions, discounting)
d. Weak field (stocky, fracture, cleavage in minerals, cleats in Coal)
e. Uniformity, alteration,
erosion f. Groundwater and hydrology
3. Geomechanical properties a.
Elastic properties (strength, elastic modulus, coefficient poison)
b. Plastic or viscoelastis behavior (flow, creep)
c. Voltage state (initial voltage,
induction) d. Consolidation, compaction
and competent e. Other physical properties (fill weight, voids, porosity, permeability, free bending, congenital bending)
Elastic properties (strength, elastic modulus, coefficient poison)
b. Plastic or viscoelastis behavior (flow, creep)
c. Voltage state (initial voltage,
induction) d. Consolidation, compaction
and competent e. Other physical properties (fill weight, voids, porosity, permeability, free bending, congenital bending)
4. Economic contingency
a. Reserves (tonnage and
levels)
b.
Production c.
Mine life d. Productivity e. Comparison of mining costs for suitable mining methods
a. Reserves (tonnage and
levels)
b.
Production c.
Mine life d. Productivity e. Comparison of mining costs for suitable mining methods
5. Technology factor
a. Mine acquisition
b. Dilusion (amount of waste
produced with ore) c. Flexibility of the method with
changes in conditions d. Selectiveity of methods
for ore and waste e. Job concentration/deployment
a. Mine acquisition
b. Dilusion (amount of waste
produced with ore) c. Flexibility of the method with
changes in conditions d. Selectiveity of methods
for ore and waste e. Job concentration/deployment
The basis in the selection of mining methods is:
1. Stripping Ratio (SR)
That is how much waste (waste soil both O/B and side rocks) that must be disposed of / removed to obtain 1 ton of ore deposits up to the ultimate pit limit.
That is how much waste (waste soil both O/B and side rocks) that must be disposed of / removed to obtain 1 ton of ore deposits up to the ultimate pit limit.
Total Waste (m3/ton) | |
SR = | ————————————- |
Total Ore (m3/ton) |
SR > 1 = Smaller stripping cost
(Tamka) SR > 1 =
Greater stripping cost (Tamda)
SR = 1 = Can Tamka/Tamda2. Break Even Stripping Ratio (BESR)
(Tamka) SR > 1 =
Greater stripping cost (Tamda)
SR = 1 = Can Tamka/Tamda2. Break Even Stripping Ratio (BESR)
That is the comparison between gross profit and O/B disposal fee.
Cost of extracting ore | |
BESR = | ————————————— |
Ob stripping cost |
To choose the mining system used the term BESR-1 for open pit i.e. overall stripping ratio.
BESR-1 > 1
= Tamka BESR-1 < 1 = Tamda
BESR
= 2 = Can Tamka / Tamda Then after the specified selected Tamka, then in order to develop a mining plan each stage used the term economic stripping ratio (BESR-2).
BESR-1 > 1
= Tamka BESR-1 < 1 = Tamda
BESR
= 2 = Can Tamka / Tamda Then after the specified selected Tamka, then in order to develop a mining plan each stage used the term economic stripping ratio (BESR-2).
Recovable value/ton ore – Production cost/ton ore | |
BESR-2 = | —————————————————————————– |
Stripping cost/ton of ore |
BESR-2 to determine the maximum number of tons of waste removed to obtain 1 ton of ore so that this mining stage still provides an advantage (max allowable stripping ratio) and to determine the pit limit.
COAL MINING SYSTEM
Mining system is a way or technique that is done to free or take the sediment of digging materials that have the economic meaning of the
parent rock to be processed further so that it can provide a great
profit with regard to the safety and safety of the best work and minimize the environmental impact that can be inflicted in order to achieve the things contained in the defenisi mining system above, then the way the mining is applied should be able to guarantee: 1. Mining costs are minimal.
2. Acquisition or mining recovery must be high.
3. Working efficiency should be high. It is affected
by : - The type of tool used.
- Good work synchronization.
- Skilled labor.
- Good organization and management.
Mining system is a way or technique that is done to free or take the sediment of digging materials that have the economic meaning of the
parent rock to be processed further so that it can provide a great
profit with regard to the safety and safety of the best work and minimize the environmental impact that can be inflicted in order to achieve the things contained in the defenisi mining system above, then the way the mining is applied should be able to guarantee: 1. Mining costs are minimal.
2. Acquisition or mining recovery must be high.
3. Working efficiency should be high. It is affected
by : - The type of tool used.
- Good work synchronization.
- Skilled labor.
- Good organization and management.
Open coal mining
Activities in open coal
mines are as follows: a. Preparation of
mining area b. Stripping and hoarding of humus
c. Stripping ground
cover d. Loading and dumping ground cover (e.g. with shovels and trucks, BWE, and dragline)
e. Coal excavation
f. Loading and transporting coal
g.
Mining flow h. Reclamation
Activities in open coal
mines are as follows: a. Preparation of
mining area b. Stripping and hoarding of humus
c. Stripping ground
cover d. Loading and dumping ground cover (e.g. with shovels and trucks, BWE, and dragline)
e. Coal excavation
f. Loading and transporting coal
g.
Mining flow h. Reclamation
Broadly, mining systems and methods are divided into 4 (four) parts, namely:
1. Surface mining.
2. Underground mining.
3. Underwater mining.
4. Insitu mining.
1. Surface mining.
Surface mining is a method of mining that all mining activities or activities are carried out above or relatively close to the surface of the earth, and its workplace is directly related to the outer air.
According to the mined material, it is divided into 4 parts, namely:
a. "Open Pit / Open Cut / Open Cast / Open Mine mining".
b. "Stripping mining". (specifically on coal mines)
c. "Quarrying mining".
d. "Alluvial Mining".
Surface mining is a method of mining that all mining activities or activities are carried out above or relatively close to the surface of the earth, and its workplace is directly related to the outer air.
According to the mined material, it is divided into 4 parts, namely:
a. "Open Pit / Open Cut / Open Cast / Open Mine mining".
b. "Stripping mining". (specifically on coal mines)
c. "Quarrying mining".
d. "Alluvial Mining".
2. Underground mining.
Underground mining is a method of mining that all mining activities or activities are carried out beneath the surface of the earth, and the workplace is not directly related to the outer air.
Underground mining is a method of mining that all mining activities or activities are carried out beneath the surface of the earth, and the workplace is not directly related to the outer air.
This underground mine is divided into 3 parts, namely:
a. Non Supported method (Open Stope Method).
b. Supported Stope Method.
c. C. Caving Method
3. Underwater mining.
Underwater mining is a method of mining whose excavation activities are carried out beneath the surface of the water or its precious mineral deposits are located below the surface of the water.
a. Non Supported method (Open Stope Method).
b. Supported Stope Method.
c. C. Caving Method
3. Underwater mining.
Underwater mining is a method of mining whose excavation activities are carried out beneath the surface of the water or its precious mineral deposits are located below the surface of the water.
According to the type of equipment used, divided into 4 types, namely:
a. Using a deep sea dredge ( > 50 m ).
b. Using hydraulic dredge.
c. C. Use a dredge with a drag net.
d. Using a deep-sea suction boat. Insitu mining
4. On-site mining
a. Using a deep sea dredge ( > 50 m ).
b. Using hydraulic dredge.
c. C. Use a dredge with a drag net.
d. Using a deep-sea suction boat. Insitu mining
4. On-site mining
Insitu mining is a method of mining that is done against specially formed mineral and rock deposits (models of certain geological deposits), where mining is directly carried out in that place in a special way.
Examples include coal gasification, pelindian method, underground heating method, methane liquefied method, etc.
Examples include coal gasification, pelindian method, underground heating method, methane liquefied method, etc.
Good Mining
Practice (GMP).
Practice (GMP).
Good mining practice (GMP) is that the entire mining process carried out from start to finish must be done properly by following established standards, following the prevailing norms and regulations so that efficient mining goals can be achieved.
One of the important parts of mining objectives is sustainable development.
Various open-pit coal
mines Grouping of coal open-pit mining types is based on the location of deposits, and mechanical tools used. Mining techniques are generally influenced by geological conditions and the topography of the area to be mined. The types of open-pit coal mines are divided into:
mines Grouping of coal open-pit mining types is based on the location of deposits, and mechanical tools used. Mining techniques are generally influenced by geological conditions and the topography of the area to be mined. The types of open-pit coal mines are divided into:
1) Contour Mining
Contour mining is suitable for coal deposits that are uncovered on mountain or hill slopes. The way of mining begins with stripping the overburden in the outcrow along the slope following the height line (contour), followed by the mining of the coal deposits. Mining continues towards the cliff until an economical sediment limit is reached when mined.
Contour mining is suitable for coal deposits that are uncovered on mountain or hill slopes. The way of mining begins with stripping the overburden in the outcrow along the slope following the height line (contour), followed by the mining of the coal deposits. Mining continues towards the cliff until an economical sediment limit is reached when mined.
According to Robert Meyers, Contour Mining is divided
into several methods, among
others: a. Conventional Contour Mining
In this method, the initial excavation is made along the hillside in the area where the coal is uncovered. The fertile of the cover soil layer is carried out by blasting and drilling or using dozers and rippers as well as front end leader loading tools, then immediately pushed and stockpiled in lower slope areas. Stripping with contour stripping will result in a bumpy, elongated and continuous operation path around the entire side of the hill.
into several methods, among
others: a. Conventional Contour Mining
In this method, the initial excavation is made along the hillside in the area where the coal is uncovered. The fertile of the cover soil layer is carried out by blasting and drilling or using dozers and rippers as well as front end leader loading tools, then immediately pushed and stockpiled in lower slope areas. Stripping with contour stripping will result in a bumpy, elongated and continuous operation path around the entire side of the hill.
b. Block-Cut Contour Mining
In this way the mining area is divided into mining blocks that aim to reduce landfill deposits during stripping of cover soil around the slopes. In the early stages of block 1 it is dug up to the heightwall which is allowed to be high. The cover land was temporarily stockpiled, the coal was then taken. After that the block 2 layer is dug up about half of it and stockpiled in block 1. While block 2 coal is ready to be excavated, then the block 3 cover soil layer is excavated and continues into the block 2 excavation cycle and stockpiles of waste soil on the initial block.
In this way the mining area is divided into mining blocks that aim to reduce landfill deposits during stripping of cover soil around the slopes. In the early stages of block 1 it is dug up to the heightwall which is allowed to be high. The cover land was temporarily stockpiled, the coal was then taken. After that the block 2 layer is dug up about half of it and stockpiled in block 1. While block 2 coal is ready to be excavated, then the block 3 cover soil layer is excavated and continues into the block 2 excavation cycle and stockpiles of waste soil on the initial block.
By the time block 1 had been stockpiled and flattened again, then the cover layer of block 4 was flattened to block 2 after the coal on block 3 was all exposed. The cover ground layer of block 5 was moved to block 3, then the cover ground layer of block 6 was moved to block 4 and so on until it was finished. This digs will reduce the number of layers of cover soil that must be transported to close the final pit.
c. Haulback Contour Mining This
haulback method is a modification of the block-cut concept, which requires a type of overburden transport, instead of directly hoarding it. So this method requires meticulous planning and operation to be able to handle coal and overburden effectively.
haulback method is a modification of the block-cut concept, which requires a type of overburden transport, instead of directly hoarding it. So this method requires meticulous planning and operation to be able to handle coal and overburden effectively.
There are three types of equipment
that are often used, namely: a. Truck or front-end
loader
b. Scrapers c. Combination of scrapers and trucks
that are often used, namely: a. Truck or front-end
loader
b. Scrapers c. Combination of scrapers and trucks
d. Box-Cut Contour Mining
In this box-cut contour mining method the covering soil layer has been excavated, stockpiled in a flat area along the outcing line to form a low embankment that will help support the largest portion of the landfill.
In this box-cut contour mining method the covering soil layer has been excavated, stockpiled in a flat area along the outcing line to form a low embankment that will help support the largest portion of the landfill.
2) Mountaintop removal method
This method of mountaintop removal method is known and developed rapidly, especially in Eastern Kentucky (USA). With this method the ground layer cover can be peeled entirely, thus allowing the acquisition of 100% coal.
3) Area mining method
This method is applied to mine coal deposits near the surface on the flat area until it is slightly ramped. The mining starts from a coal outs that have a layer and shallow cover soil continues to the thicker to the pit boundary.
There are three ways of mining the area mining method, namely:
A. Conventional area mining method
In this way, excavation begins in the initial mining area so that the excavation of the covering soil layer and its hoarding does not interfere with the environment too much. Then this layer of cover soil is stockpiled behind the mined area.
B. Area mining with stripping shovel
This is used for coal located 10–15 m below ground level. Mining starts by creating a rectangular opening. The cover layer is stockpiled parallel to the direction of excavation, in the area being mined. This parallel excavation is carried out until the entire sediment is excavated.
C. Block area mining
This method is almost the same as conventional area mining method, but the mining area is divided into several mining blocks. This is limited to coal deposits with a maximum cover layer thickness of 12 m. The initial excavation blocks were made with bulldozers. The excavation soil is then pushed in the area adjacent to the excavation area.
4) Open pit Method
This method is used for coal deposits that have a large and steep dip. The coal deposits should be thick when the cover layer is thick enough.
This method is used for coal deposits that have a large and steep dip. The coal deposits should be thick when the cover layer is thick enough.
a. Oblique
coating This way can be applied to coal layer consisting of one layer (single seam) or more (multiple seam). In this way a layer of ground cover that has been able to be stockpiled on both sides on each stripping.
coating This way can be applied to coal layer consisting of one layer (single seam) or more (multiple seam). In this way a layer of ground cover that has been able to be stockpiled on both sides on each stripping.
b. Thick coating
In this way mining begins by stripping the cover soil and hoarding is carried out on the already mined area. Before starting, there must first be sufficient outal area to be used as a hoarding area in the next operation.
In this way mining begins by stripping the cover soil and hoarding is carried out on the already mined area. Before starting, there must first be sufficient outal area to be used as a hoarding area in the next operation.
In this way, both in stripping the ground cover and extracting coal, benching system is used.
1.2 Underground coal mining
Underground coal mining method there are 2
popular pieces, namely: - Room and Pillar
- Longwall
popular pieces, namely: - Room and Pillar
- Longwall
1.2.1 Room and Pillar
This method of mining is characterized by leaving the pillars of coal as natural buffers. This method is commonly applied to areas where subsidence is not permitted. The Layout of the Room and Pillar Method can be seen in The Image. This mining can be done manually or mechanically.
1.2.2 Longwall
This method of mining is characterized by creating mining panels where roof rock impacts are allowed to occur behind the excavation area. The Layout of the Longwall Method can be seen in The Image. This mining can also be carried out manually as well as mechanically.
1.3 Auger Mining
Auger mining is a method of mining for surfaces with high walls or the discovery of outcrop recovery (outcrop recovery) of coal by drilling or digging openings into the layer between the layers of the cover. Auger mining was born before the 1940s is a method of obtaining coal from the left side of the high wall after conventional surface mining. Coal mining with auger works on the principle of large-scale drag bit rotary drill. Without damaging the coal, the auger extracts and raises the coal from the hole by tilting the conveyor or loading it using a loader into the truck.
The development and preparation of the area for auger mining is an easy task if done in conjunction with the use of open cast or open pit methods. After high wall conditions, auger drilling can be placed on site. The sediment conditions that can use this method based on Pfleider (1973) and Anon (1979) are deposits that have a good spread and the slope is close to horizontal, as well as the depth is shallow (limited to the height of the wall where the auger is placed.
PICTURES – PICTURES
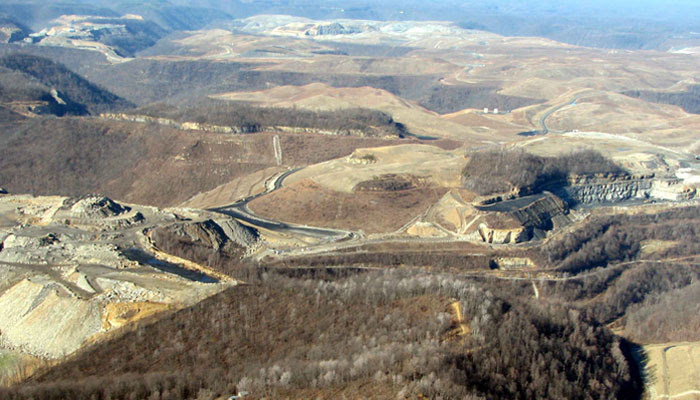
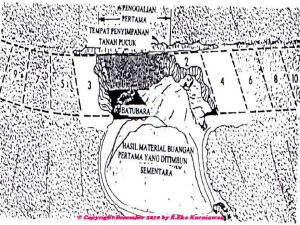
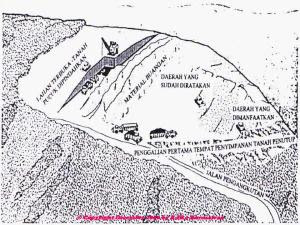
- Open Pit Mining
Bantu berikan donasi jika artikelnya dirasa bermanfaat Anda dapat berkontribusi dengan mengeklik tautan di bawah ini:
Donasi Sekarang
































Komentar